2nd day of TPM meeting at Timisoara
22 03 2022We assist to the TPM meeting held on 22nd March 2022, Timisoara, Romania. 3D printing support service for innovative citizens (INNO3D).

more info at «https://www.inno3d.eu/»
Categories : Materiales
We assist to the TPM meeting held on 22nd March 2022, Timisoara, Romania. 3D printing support service for innovative citizens (INNO3D).


more info at «https://www.inno3d.eu/»
We assist to the TPM meeting held on 21 st and 22 nd March 2022, Timisoara, Romania.3D printing support service for innovative citizens (INNO3D). MEETING LOCATION: Central University Library of Politehnica University of Timisoara, ROMANIA




Today, January 27th, we’ve participated on the DAY 2 of the INRS Project Kick off Meeting hosted by Technological University of the Shannon (TUS): Midlands Midwest. We participate on the Developing Information and Research Skills for Business, Innovation and Entrepreneurship (INRS) Project.
Today, January 26th, we’ve participated on the DAY 1 of the INRS Project Kick off Meeting hosted by Technological University of the Shannon (TUS): Midlands Midwest. We participate on the Developing Information and Research Skills for Business, Innovation and Entrepreneurship (INRS) Project.
The last saturday january 22th, has been imparted under Dismold Master, the inno3d training event.
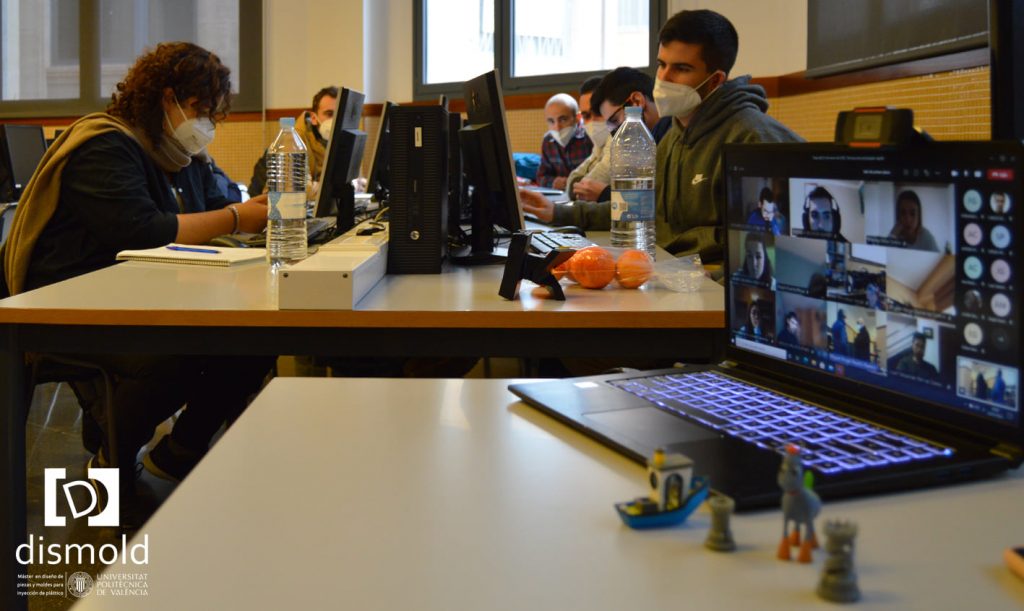
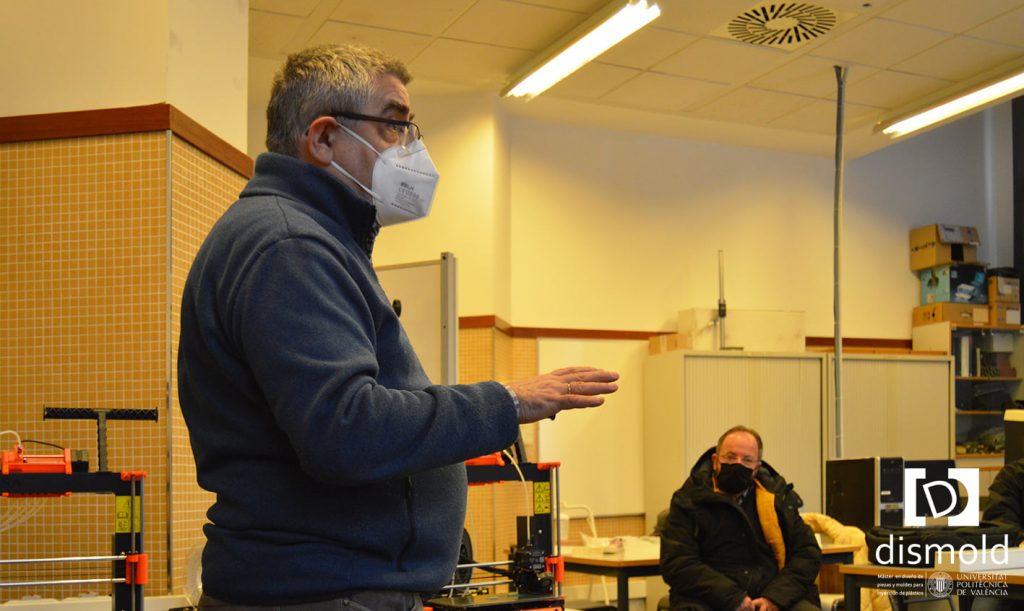





more info https://www.inno3d.eu/
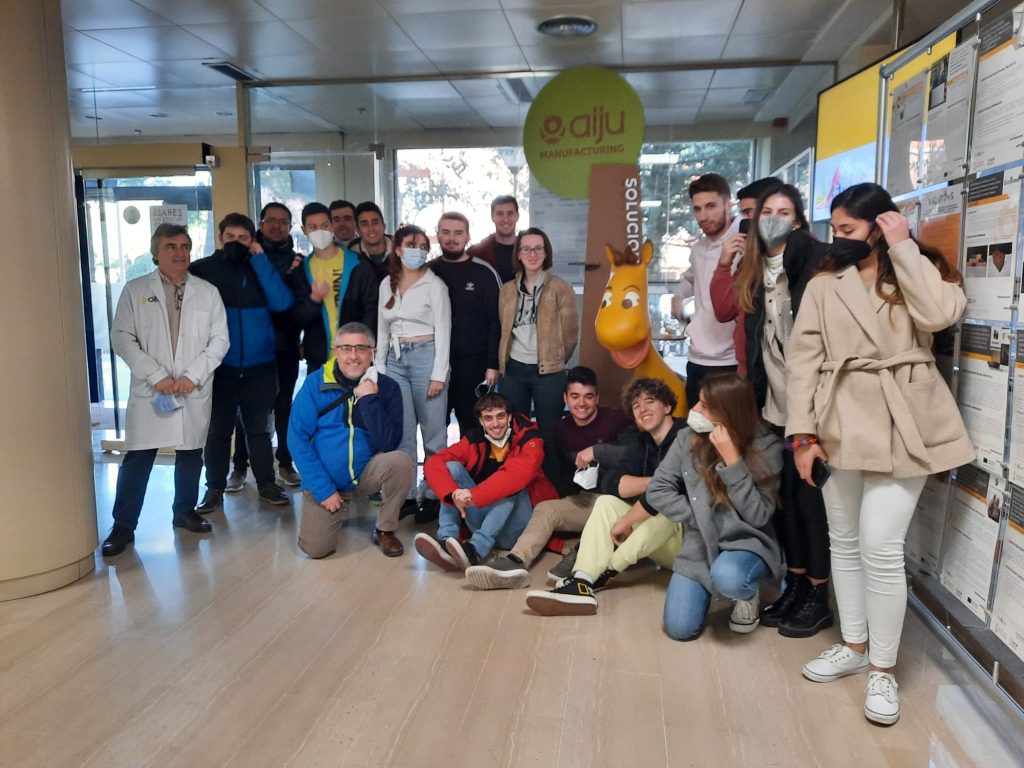
Hoy, 20 de diciembre del 2021, hemos visitado el área de impresión 3D y fabricación aditiva de Aiju.


We participated in the meeting (7th-11th November 2021) about 3D printing INNO3D Erasmus+ project. These are our colleagues partners.
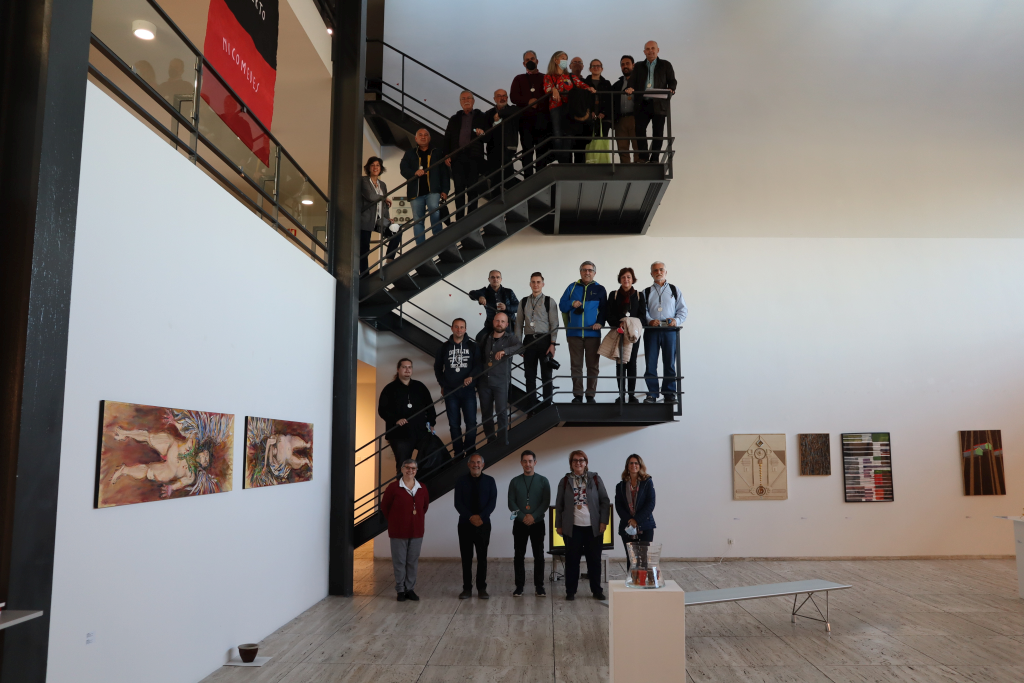


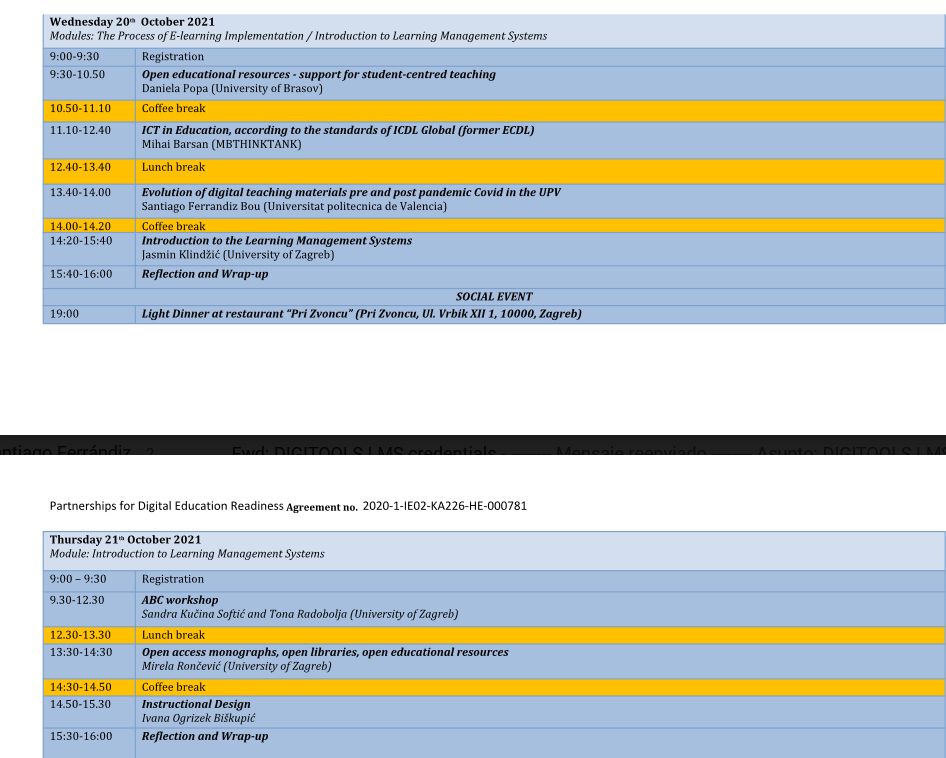
The Short-term Joint Staff Training of Innovative Tools for Enhancing E-Learning Solutions in Universities (DIGITOOLS), has been started on 19th October 2021. We used and Hybrid mode, face to face and online, together between 19th and 22nd October. It takes place at the University of Zagreb, Croatia.